How to Install MongoDB 4.2 on Ubuntu 16.04
Categories:
Introduction
In this tutorial, we will learn how to install MongoDB 4.2 on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus).
What is mongoDB? from MongoDB website:
MongoDB is a document database with scalability and flexibility that you want with query and indexing that you need.
Prerequisites
- Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus) with sudo access
Add MongoDB Repository
First of all, let’s add the MongoDB public key. This key is used by package management tool like apt to ensure the consistency and authenticity of the package.
wget -qO - https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.2.asc | sudo apt-key add -
The output of command above should be OK. If you have different output then you need to fix the error first.
Create new file /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.2.list that contain MongoDB 4.2 repository info using command below
echo "deb [ arch=amd64 ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu xenial/mongodb-org/4.2 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.2.list
Reload package database using the command below
sudo apt-get update
Install MongoDB 4.2
To install the latest stable version of MongoDB 4.2 you can use the command below. At the time of this writing, the latest stable version of MongoDB 4.2 is 4.2.2.
sudo apt-get install mongodb-org
We can also install previous stable version of MongoDB from repository.
Instead of only providing one package name, we have to list all packages that we want to install with specific version
For example, if you need to install MongoDB 4.2.0 you can use the command below.
sudo apt-get install -y \
mongodb-org=4.2.0 \
mongodb-org-server=4.2.0 \
mongodb-org-shell=4.2.0 \
mongodb-org-mongos=4.2.0 \
mongodb-org-tools=4.2.0
Managing MongoDB Service
We can check or verify whether MongoDB already installed using dpkg command.
dpkg -l | grep mongodb
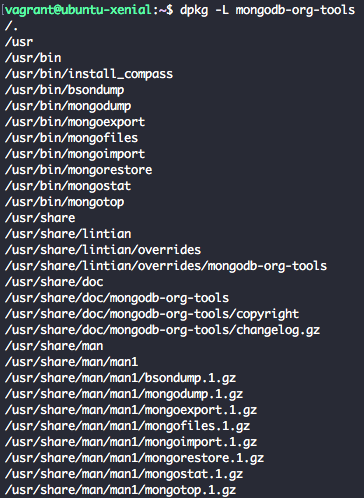
To get list of files installed for a package we can use the command below
dpkg -L mongodb-org-tools
Now MongoDB installed let’s check MongoDB service using command below:
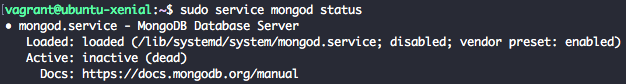
sudo service mongod status
or we can use command below:
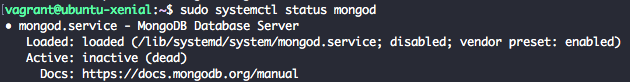
sudo systemctl status mongod
We will get output similar to below which inform that mongod is not running.
To start MongoDB service we can use command below:
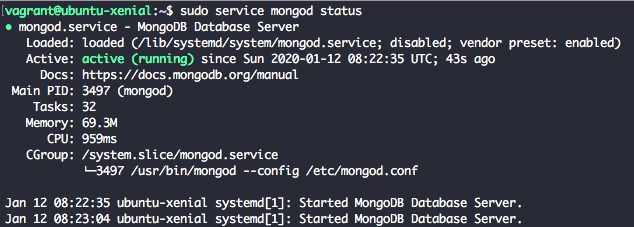
sudo service mongod start
or we can also use systemctl to start MongoDB service
sudo systemctl start mongod
We will see output similar to output below
MongoDB service already started but it’s not enabled by default by seeing this line
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mongod.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Let’s enable MongoDB service on boot by running
sudo systemctl enable mongod
Now if we check MongoDB service status we will see that the service is enabled.
Checking MongoDB Service
Beside using service or systemctl command, we can check MongoDB service status using several tools.
To check where MongoDB service listening to we can use netstat
sudo netstat -naptu | grep 27017
We grep MongoDB default port 27017.
As alternative we can also grep mongod application name
sudo netstat -naptu | grep mongod
We can also use ss to do similar check like netstat
ss -at | grep 27017
To check MongoDB service process we can use command below.
ps aux | grep -m1 mongod
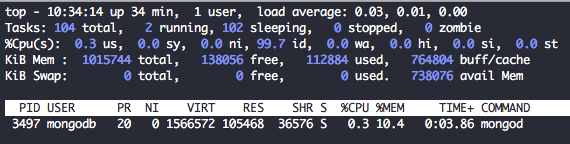
For a more detailed info of MongoDB process, we can use top and only show process run by mongodb user.
top -u mongodb
 Creating root and admin users
Creating root and admin users
MongoDB user management is different compared to RDBMS user management like MySQL or PostgreSQL.
In MongoDB the user is managed per database. If you want to create administrative user you need to create user in admin database.
Connect to MongoDB using mongo client
mongo
Use command below to create user root with root role. Don’t forget to change the password.
db.createUser({user:"root", pwd:"changemeplease123123123", roles:[{role:"root", db:"admin"}]})
To generate random string for password on command line you can use comand below
uuidgen | sha256sum | awk {'print $1'}
or
uuidgen | sha256sum | cut -d ' ' -f 1
Enabling Authentication
There are two ways to enable MongoDB authentication, by updating systemd service file or updating mongodb.conf file.
I recommend using the second method since mongodb service file might be overwrite by apt when we upgrade mongodb package.
Updating mongod.service file
Open /lib/systemd/system/mongod.service file.
Find line
ExecStart=/usr/bin/mongod --config /etc/mongod.conf
Replace the line with
ExecStart=/usr/bin/mongod --auth --config /etc/mongod.conf
Reload systemd daemons
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Restart MongoDB service.
sudo systemctl restart mongod
Updating mongodb.conf file
Open ``/etc/mongodb.conf file
Find line
#security:
Replace it with
security:
authorization: enabled
Restart MongoDB service to enable authentication
sudo service mongod restart
After enabling authentication we can connect using root user that we just created on previous step.
mongo -uadmin admin -p
Uninstall MongoDB 4.2
In this section we’ll learn how to uninstall MongoDB 4.2 from Ubuntu 16.04. Please be really careful when running command on this section.
Before we uninstall MongoDB 4.2 we need to stop MongoDB service first.
sudo service mongodb stop
We can remove MongoDB packages using command below
sudo apt-get purge mongodb-org*
Now we can remove MongoDB log directory by running the following command
sudo rm -r /var/log/mongodb
Last directory that we need to remove is MongoDB data directory, use command below
WARNING : command below will remove your data and cannot be restored. be very very very careful when you’re running command below.
sudo rm -r /var/lib/mongodb
MongoDB 4.2 References
You can find references related to MongoDB 4.2 below
- MongoDB 4.2 Manual
- MongoDB 4.2 Release Notes
- MongoDB 4.2 FAQ
- Configuration file options
- MongoDB 4.2 What’s New (pdf)
Conclusion
In this article, you set up MongoDB 4.2 on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus). After that, you also learn how to manage MongoDB service, check MongoDB service status using multiple tools, create root user and also enable authentication.
At the end we learned how to uninstall MongoDB 4.2 from Ubuntu 16.04.
Now you can start building your application using MongoDB as a database.